To really understand this concept, we need to know the main
type of power we have in an AC circuit which are:
- Active Power or True Power
- Reactive Power and
- Apparent Power
- Active or True Power is the power that is actually been
delivered to load I mean the useable power that your generator outputs and its
denoted in KiloWatt or Watts. By formula; P=IV or I^2 x R(watts)
- Reactive Power is the power used to establish and maintain the
magnetic field also it can be thought of as power that is stored in the generator and released back into the source through AC. By formula; Q =
I2X Where X is the reactance in Ohms.
Reactive power is basically there due to the presence of
inductive or capacitive components in an AC circuit because when current flows
through this components some certain amount of power will be dissipated. It can be think of as power due to loss.
- Apparent Power is the total power of both the Reactive and
Active power. By formula; S = I2
Z. Where Z is the total reactance i.e sum of resistance and reactance known as Impedance.
Below is the circuit with reactive component precisely an inductor
Below is the circuit with reactive component precisely an inductor
 |
| Inductive circuit |
 | |
| The Circuit total impedance |
KVA is the unit of apparent power denoted with (S) and one of the very reason is that generators have windings in them and it is this windings that make them an inductive load and exhibit the so called inductive property and Inductive load are loads which there current lags voltage by an angle of 900 and obviously the inductor is the culprit because every half cycle it stores energy in its magnetic field and return it there are still some extra energy that sloshes back and forth between the windings of the generator. It is this back and forth energy transfer that causes the current to be out of phase with the voltage.
One other reasonable reason is that in winding component of a generator
there use to be some losses such as Copper loss and Core loss which actually constitute the reactive behavior of a generator.
* Copper or I2R Loss is the loss due to the winding
resistance and it strongly affects the current characteristics and output capacity of
the generator. It basically occurs when current begins to flow through the
winding of the coil and it however results to heat been developed over time on
the conductor used for the winding which means the higher the current applied
to the generator the higher will be its copper loss and the lesser will be its
output deliver power but this abnormality can however be control by using
larger cross sectional area of the conductor.
* Core Losses are losses due to the alternating magnetic field
in the core material used for the winding and as the frequency increases the
two properties of core loss which are hysteresis loss and eddy current losses
increase there by affecting the output characteristics.
In reality, the core of a generator is not the electrical part
that actually carries the current but just aid in the magnetic induction of the
internal conductor but still supports to generator losses
The eddy current loss is the loss that is actually responsible
for the loss due to the sinusoidal effect on the core which causes some portion
of EMF to be induced on the core material used in the generator
* The Hysteresis Loss however is due to the difference in loading and unloading of magnetic energy in the core and causes heating of the core material.
So, in essence the copper loss depends on current while the
iron loss depends on voltage.
Because of these two losses the generator rating will not be
in KiloWatt (KW) but in KiloVoltAmp so that we will be able to account for
these two losses.
Power Factor (P.F) is also a function of this KVA and even KVAR rating also because it actually determines the efficiency of the generator and its value is always less than unity mostly 0.8. The losses explain above also contribute to the power factor of the generator which practically is always less than unity resulting to decreasing in the overall output efficiency. This effect can easily be noted using the mathematical relation between Real and Reactive Power.
This scenario is the basic reason why the generator can never expressed in KW but rather KVA
Resistive load are the unmotorized load and they tends to
convert all the electrical power in the form of heat but the inductive load
stored some of the energy in the form of an electromagnetic field
Example of inductive load are: motors, transformers, bulb, kettle, toaster e.t.c
In Summary
In Summary
The major reason why your generator is rated in KVA is because KVA is a unit of apparent power which is the sum of the active power and reactive power and because your generator is made of reactive components precisely coils of conductor it makes your generator to have reactive property.
Reactive effect/ property leads to some certain losses of power which has to be account for.
The active power of your generator is typically the useful power you get as your generator output when you connect a meter to its output while the reactive power is the one that is due to losses been generated inside the generator either loss to the conductor winding(Copper loss) or the core material(core loss) used in the construction of the motor.
So the apparent power is just the sum of both the reactive(unuseful power) and active power(useful power) of your generator
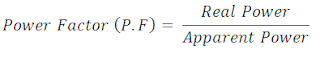
Thanks for sharing
ReplyDelete